Understanding Cyber Threats

Cyber threats refer to malicious activities conducted through the use of electronic devices and networks with the intent of disrupting, accessing, stealing, or destroying sensitive information. These threats can come in various forms, including malware, phishing attacks, ransomware, and denial of service attacks.
One of the biggest challenges with cyber threats is that they are constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated as technology advances. This makes it difficult for organizations and individuals to protect themselves from potential attacks.
To mitigate cyber threats, it is important to have robust cybersecurity measures in place, such as firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, and regular security updates. It is also crucial to educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as using strong passwords, being cautious of email attachments and links, and avoiding sharing sensitive information online.
In addition, organizations should have an incident response plan in place to quickly identify and respond to cyber threats if they occur. This may involve working with cybersecurity experts to analyze the threat, contain the breach, and mitigate any damages.
Implementing Cyber Security Measures
It is important for organizations to implement cyber security measures to protect their sensitive data and systems from cyber threats. Here are some steps that can be taken to enhance cyber security measures:

1. Implement strong passwords and multi-factor authentication:
Encourage employees to create strong passwords that are difficult to guess and enable multi-factor authentication for an extra layer of security.
2. Keep software and systems up to date:
Regularly update software and systems to ensure they are protected against known vulnerabilities and exploits.


3. Use firewalls and antivirus software:
Install firewalls and antivirus software to monitor and protect your network from malicious attacks and viruses.
4. Educate employees on cyber security best practices:
Provide training and resources to educate employees on how to spot phishing emails, avoid clicking on suspicious links, and protect sensitive information.

5. Monitor network activity:
Use intrusion detection systems and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to monitor network activity and detect any suspicious behavior.
6. Implement access controls:
Limit access to sensitive data and systems only to authorized personnel and regularly review user permissions to prevent unauthorized access.


7. Backup data regularly:
Regularly backup important data to a secure location to ensure that it can be recovered in case of a cyber attack or data breach.
8. Conduct regular security audits:
Regularly assess your organization’s cyber security posture through security audits and penetration testing to identify and address any vulnerabilities.


9. Develop an incident response plan:
Create a detailed incident response plan outlining the steps to be taken in case of a cyber security incident, including communication protocols and processes for containing and mitigating the damage
10. Stay informed about emerging threats:
Stay up to date on the latest cyber security threats and trends by monitoring industry reports, attending conferences, and collaborating with other organizations in your industry to share best practices.

Securing Your Online Presence
In today’s digital age, it is more important than ever to secure your online presence to protect your personal information and privacy. Here are some tips to help you secure your online accounts and data:

1. Use strong, unique passwords:
Use different passwords for each of your online accounts and make sure they are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Consider using a password manager to securely store and generate complex passwords.
2. Enable two-factor authentication:
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or email, in addition to your password.


3. Keep your software up to date:
Make sure to regularly update the software on your devices and apps, as updates often include important security patches that help protect against vulnerabilities.
4. Be cautious of phishing scams:
Be wary of emails or messages that ask for sensitive information or contain suspicious links. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown senders and always verify the authenticity of requests for personal information.


5. Secure your social media accounts:
Check your privacy settings on social media platforms to control who can see your posts and information. Be mindful of the information you share online, as it can be used by cybercriminals for phishing attacks or identity theft.
6. Use secure connections:
When using public Wi-Fi networks, avoid accessing sensitive information or making online transactions unless you are using a secure connection, such as a virtual private network (VPN).


7. Monitor your accounts:
Regularly review your online accounts for any unauthorized activity or suspicious changes. Report any unusual activity to the account provider and take immediate steps to secure your account.
Enhancing Data Protection
Data protection is a critical consideration for individuals, businesses, and organizations in today’s digital age. As more and more data is collected, stored, and shared online, it is important to take steps to enhance data protection and safeguard sensitive information.

1. Implement strong encryption:
Encryption is a powerful tool that helps secure data by encoding information in a way that can only be decrypted with the appropriate key. Implementing strong encryption protocols can help protect data both in transit and at rest.
2. Use multi-factor authentication:
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before granting access to sensitive data. This can help prevent unauthorized access even if login credentials are compromised.


3. Regularly update software and systems:
Keeping software and systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates is essential for protecting against vulnerabilities and potential cyber attacks. Regularly updating software can help to minimize the risk of data breaches.
4. Implement access controls:
Limiting access to sensitive data to only those employees who need it can help reduce the risk of data breaches. Implementing access controls, such as role-based access control, can help ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information.


5. Train employees on data protection best practices:
Educating employees on data protection best practices, such as how to create secure passwords, how to recognize phishing attempts, and how to handle sensitive information, can help prevent data breaches caused by human error.
6. Conduct regular security audits and assessments:
Regularly assessing your organization’s security posture can help identify potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Conducting security audits can help ensure that data protection measures are effective and up to date.
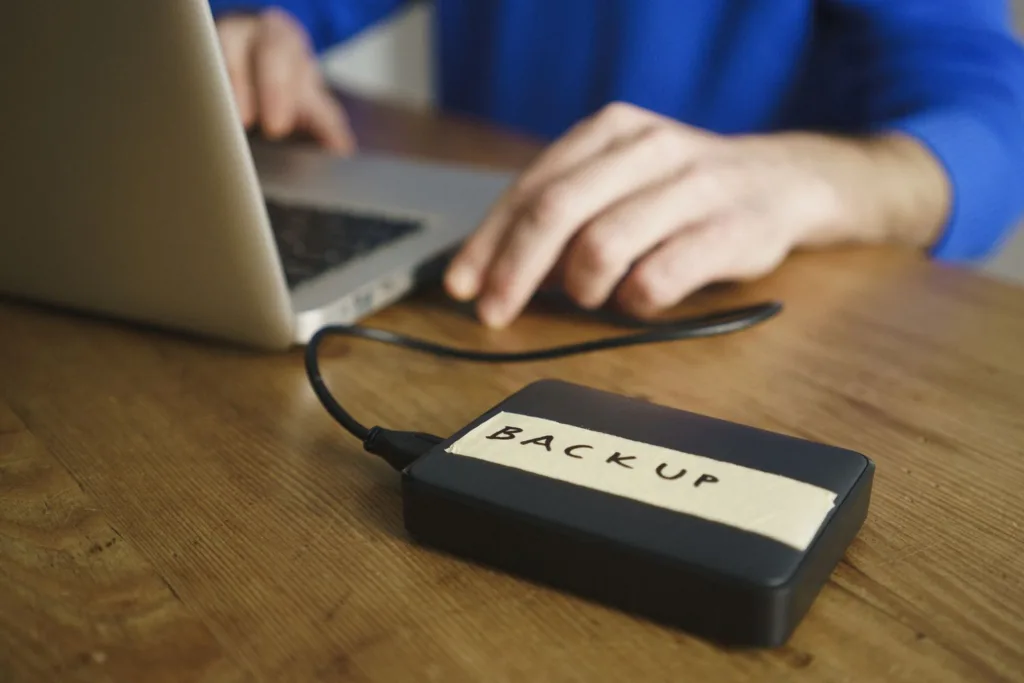


7. Backup data regularly:
Regularly backing up data can help ensure that you have access to a clean, secure copy of your information in the event of a data breach or loss. Implementing automated backup procedures can help streamline the backup process and ensure that critical data is protected.









