Dark web, Deep web and some misconceptions about them
WHAT IS THE DARK WEB?
The dark web is a part of the web that isn’t filed via web indexes. You’ve presumably heard discussion of the “dark web” as a hotbed of crime — and it is. Researchers Daniel Moore and Thomas Rid of King’s College in London classified the 2,723 contents of live dark web sites over a five week period in 2015 and found that the dark web hosts 57% illegal content.
A report of 2019, Into the Web of Profit, directed by Dr. Michael McGuires at the University of Surrey, shows that things have become more unpleasant. The quantity of dark web postings that could harm an organization has ascended by 20% from 2016. Of all postings, 60% might actually harm ventures.
You can purchase credit card numbers, every kind of drug, guns, fake money, hacked Netflix accounts and software that assists you with breaking into other people’s computers.
Not everything is illegal, the dark web also has a legitimate side. For example, you can join a chess club or BlackBook, a social network described as “the Facebook of Tor.”
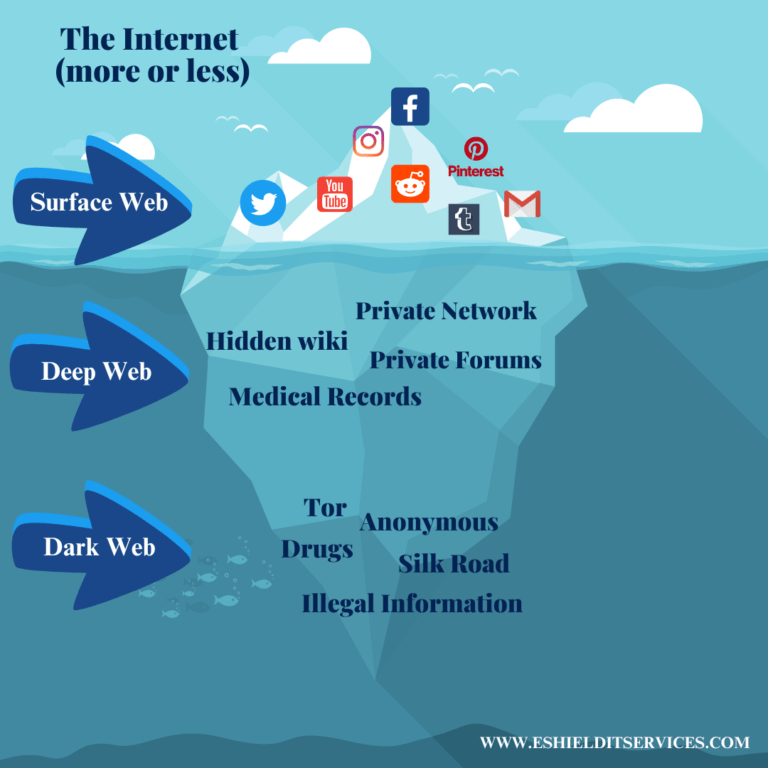
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEEP WEB AND DARK WEB?
People often use the terms “deep web” and “dark web” interchangeably, but they are not the same. Deep web refers to anything on the internet that is not indexed by and, therefore, accessible via a search engine like Google. Deep web content incorporates anything behind a paywall or requires sign-in credentials. Deep web also includes content which is blocked by the owners from indexing.
Health records, content that needs a subscription, membership sites, and confidential corporate information are a few examples of what makes up the deep web. Estimates place the size of the deep web at between 96% and 99% of the internet. Just a small part of the web is open through a standard internet browser — commonly known as the “clear web”.
The dark web is a subset of the deep web that is deliberately hidden, requiring a particular browser— Tor — to access. Nobody truly knows the size of the dark web, yet most estimates put it at around 5% of the internet. Again, not everything about the dark web is utilized for unlawful purposes regardless of its unpropitious sounding name.
TOOLS AND SERVICES
The Into the Web of Profit report identified 12 categories of tools or services that could present a risk in the form of a network breach or data compromise:
- Infection or attacks, including malware, distributed denial of service (DDoS) and botnets
- Access, including remote access Trojans (RATs), keyloggers and exploits
- Espionage, including services, customization and targeting
- Support services such as tutorials
- Credentials
- Phishing
- Refunds
- Customer data
- Operational data
- Financial data
- Intellectual property/trade secrets
- Other emerging threats
The report also outlined three risk variables for each category:
- Devaluing the enterprise, which could include undermining brand trust, reputational damage or losing ground to a competitor.
- Disrupting the enterprise, which could include DDoS attacks or other malware that affects business operations.
- Defrauding the enterprise, which could include IP theft or espionage that impairs a company’s ability to compete or causes a direct financial loss.
Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) has been accessible on the dark web for quite a long time, however those contributions have become undeniably more risky and dangerous with the ascent of specific criminal groups like REvil or GandCrab. These groups create their own malware, sometimes combined with pre-existing tools, and distribute them through “affiliates”.
The affiliates disseminate the ransomware bundles through the dark web. These attacks frequently incorporate stealing their targets’ confidential information and threatening to post it on the dark web if the ransom is not paid.
Tor Browser
This activity, this vision of a marketplace, could make you imagine that exploring the dark web is simple and easy. But it isn’t. Dark web is chaotic place as everyone is anonymous, and filled with cyber criminals trying to scam others. Accessing the dark web requires the use of an anonymizing browser called Tor. The Tor browser routes your web page requests through a series of proxy servers operated by thousands of volunteers around the globe, rendering your IP address unidentifiable and untraceable. Tor works like magic, but the result is an experience that’s like the dark web itself: unpredictable, unreliable and maddeningly slow.
SEARCH ENGINE
With regards to the best dark web search engines, there are a couple of things to remember. First, you need a search engine that is private and secure, and can be used anonymously. Additionally, you want a search engine that is fast and efficient, so you can get the information you need without any delays. Some of the best dark web search engines are:
- Pipl
- Ahmia.fi
- Haystak
- The Hidden Wiki
- Torch
- Recon
- DuckDuckGo
- Onion Search
CAN SOMEONE SELL MY DATA ON THE DARK WEB?
It’s right on the money to expect that your own data is on the dark web. In any instance when your personal information can be seen on the dark web search engines, it is most likely to be found on the dark web too. There are three ways your personal details end up on the internet, be it on the visible World Wide Web, part of the Deep Web, or on the Dark Web:
- Through your passive digital footprint (metadata): The information you incidentally leave online when you use the internet. This incorporates your IP address (which also uncovers your geographical location), what sort of devices you use, the sites you visit(browsing history), the kind of internet browser and web search tools you’re utilizing (Chrome, Firefox, etc.), and many more details.
- Through your active digital footprint: This addresses the data you readily post on the web — from pictures to videos, articles, and other details you unveil when you make purchases on the web (physical, telephone numbers, etc.) and when you interact with service providers, friends, and a host of other entities.
- Through information other entities disclose about you: This incorporates government agencies, organizations that deal with credit reports, and information brokers that harvest and compile information about you so they can sell your profile to organizations that need to target you with promotions.
IS THE DARK WEB ILLEGAL?
Not everything on the dark web is illegal. The Tor network started as an anonymous communication channel, it actually fills an important need in assisting individuals with imparting in conditions that are unfriendly to free speech.
If you have any desire to learn about privacy protection or cryptocurrency, the dark web brings a lot to the table. There is an assortment of private and encrypted email services, directions for installing an anonymous operating system, and tips for the privacy-conscious.
There’s also material that you wouldn’t be surprised to find on the public web, such as links to full-text editions of hard-to-find books, collections of political news from mainstream websites, and a guide to the steam tunnels under the Virginia Tech campus. You can conduct discussions about current events anonymously on Intel Exchange. There are several whistleblower sites, including a dark web version of Wikileaks. Pirate Bay, a BitTorrent site that law enforcement officials have repeatedly shut down, is alive and well there. Even Facebook has a dark web presence.
There are enough practical values for some organizations. Law enforcement agencies keep an eye on the activities that happen on the dark web and look for stolen data. Numerous established press associations monitor whistleblower sites searching for news.
Please visit our Services page for a full range of services offered.


